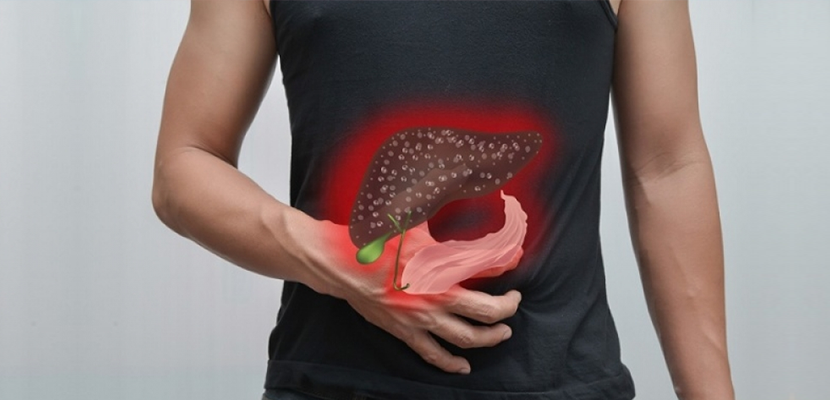
Our liver is one of the most vital organs in our body, and yet, not many know its functions.
The liver is situated at the upper right-hand part of the abdominal cavity, below the diaphragm and above the stomach and intestine. The liver produces a liquid called bile, which helps break down fats in the small intestine during digestion and carry the waste material from the liver for excretion. It produces cholesterol and certain proteins to carry fats through the body. It also produces some proteins for the blood plasma. Liver stores glucose (in the form of glycogen), which can be released when glucose is required by the body. Also, the liver removes drugs and other toxic
substances from the blood.
As the liver is involved in various functions, it can also be associated with several medical conditions, one of which is fatty liver. As the name suggests, fatty liver is a condition in which extra fat is deposited in the liver over a period of time.
There are several myths and misconceptions around fatty liver diseases. This article debunks the myths and presents the facts surrounding the fatty liver disease.
Table Of Contents
- Myth 1: Fatty Liver is not a Serious Condition
- Myth 2: Only Alcoholics can get Fatty Liver
- Myth 3: Drinking Hard Liquor is Worse than Drinking Beer or Wine
- Myth 4: Fatty Liver Cannot be Reversed
- Myth 5: Women are more Likely to Develop Fatty Liver
- Approach us
Myth 1: Fatty Liver is not a Serious Condition
Normally, a healthy liver contains some amount of fat. When the fat built-up is more than 5 percent of the total weight of the liver, then the condition is called fatty liver disease. Accumulation of excess fat in the liver affects the metabolic processes and can result in severe problems in the entire body.
According to a study, the incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, a type of fatty liver, in India ranges from 9% to 32% in the general population. The condition is prevalent among individuals with diabetes, prediabetes, overweight or obesity.
Fatty liver does not manifest any symptoms; thus, many people may not know if they have the condition. However, if left untreated, the accumulation of fat can cause damage to the liver cells and lead to inflammation. Fatty liver can progress into liver cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), build-up of fluid in the abdomen, confusion, drowsiness, liver cancer and liver failure.
Myth 2: Only Alcoholics can get Fatty Liver
Fatty liver can occur due to alcohol consumption, as well as, non-alcoholic causes. Based on the causes, fatty liver has two types – non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (also known as alcoholic steatohepatitis).
NAFLD is a type of fatty liver, in which the excess fat deposition is not caused by heavy alcohol consumption. Th exact cause of the condition is not known, it has several contributing factors, including obesity, diabetes, high blood cholesterol, viral hepatitis, certain autoimmune conditions, and some medications.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is directly related to heavy alcohol use. The alcohol present in the blood is metabolised by the liver, which results in the production of harmful substances that can damage liver cells and induce inflammation. As the alcohol consumption increases, the extent of liver damage also increases. If alcohol consumption is not stopped, it can lead to alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Myth 3: Drinking Hard Liquor is Worse than Drinking Beer or Wine
The type of alcohol consumed does not have different effect on the liver. It is the amount of alcohol consumed that must be controlled.
The ‘safe’ amount of alcohol to be consumed, depends on the body weight, genetic factors, size and gender. The risk of liver damage is higher in women than men, as they absorb more alcohol from each drink. Women with a healthy liver should not have more than one alcoholic beverage per day, men should not have more than two drinks per day. One drink may include 1½ ounces of liquor, 12 ounces of beer or 5 ounces of wine.
Having more alcohol than the individual limits, can harm the liver. If the person already has a liver disease, they should abstain from alcohol, no amount is safe for them.
Myth 4: Fatty Liver Cannot be Reversed
Fatty liver does not have any a specific treatment or any drugs. However, fortunately, fatty liver caused by both alcohol and non-alcohol related causes can be reversed by making healthy lifestyle choices, which includes the following:
- Avoiding alcohol
- Reducing sugar intake
- Decreasing high-fat foods
- Having lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Maintaining health body weight
- Exercising regularly
Losing only 3% to 5% of the total body weight can reduce the fat content in the liver. For individuals with less severe forms of alcoholic fatty liver disease, only two weeks of not drinking can help undo the liver damage. Although, if the person resumes drinking the damage can occur again.
Myth 5: Women are more Likely to Develop Fatty Liver
Studies suggest that women are less likely to develop NAFLD than men. But once diagnosed, women have a higher risk of advanced fibrosis, especially after the age of 50 years. However, this remains a controversy among experts.
Approach us
For the best treatment and management of fatty liver disease, please contact us via email or telephone calls. Our gastroenterologist, Dr. Parthasarathy, will clarify if you have any doubts and will help you reverse your fatty liver disease.
Dr. Parthasarathy is one of the most renowned surgical gastroenterologists in Hyderabad, India. He has about 15 years of experience and has performed 3000+ advanced laparoscopic procedures. He has been trained by the best institutes in the country and abroad.